 |
| Position of Neptune in Aquarius. Credit: Astronomy.com |
Over the next couple of days, our planet Earth's orbit will pass directly between Neptune and the Sun. Looking at the three on edge, they will appear with their equators in line across the Solar System. This alignment is referred to as opposition – opposite the sun in Earth’s sky - that planet is the closest it will be to the Earth for the year. Typically, the planet will shine brightly and be easy to
 |
| Locating Neptune in Aquarius Credit: EarthSky.com |
Neptune's opposition will occur on September 1st and on that night, the planet will rise in the east around sunset, climb to its peak in the sky by midnight, and then set in the west around sunrise.
The best way to locate Neptune is to first find the constellation Aquarius (The Water Carrier). Spatially speaking, it's closer than the constellation and should appear in front of it. Then you need to consult a detailed Star Cart so that you know all of the stars that are ordinarily visible in that area. Then look for that dimmest of specks that doesn't belong.
Facts About Neptune:
A Neptonian Day is about 18 hours, with the ice giant spinning like a dervish on its axis.
By contrast, it's year - the time to orbit the Sun - is roughly 165 Earth years.
It's the stormiest planet with wind speeds that break the sound barrier.
Eventually, it's strong gravitational pull will destroy its moon, Triton.
It appears as a
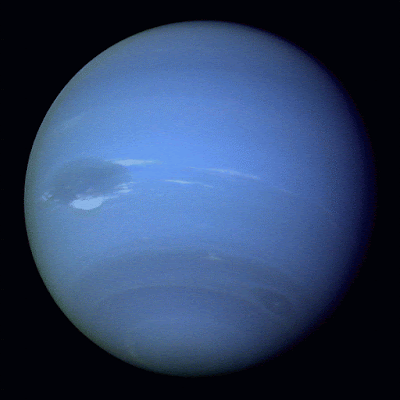 |
| Neptune as photographed by Voyager 2 Credit: EarthSky.com |
The Voyager 2 flyby revealed Neptune appearing as a bright, azure blue planet with a deep blue spot not unlike Jupiter's red spot. The blue color is due to the presence of methane in its outer atmosphere. Planetary "color" is a function of reflected light from the Sun. When the Sun's light hits the atmosphere, the methane absorbs the light in the red spectrum and reflects back the blue light, giving the planet the appearance of a bright blue orb.
References:
EarthSky http://earthsky.org/tonight/neptune-comes-closest-to-earth-for-the-year-on-august-31
Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neptune
Space Facts http://space-facts.com/neptune
Universe Today http://www.universetoday.com/21591/color-of-neptune/
Astronomy http://www.astronomy.com/observing/sky-this-week/2015/08/august-28september-6-2015